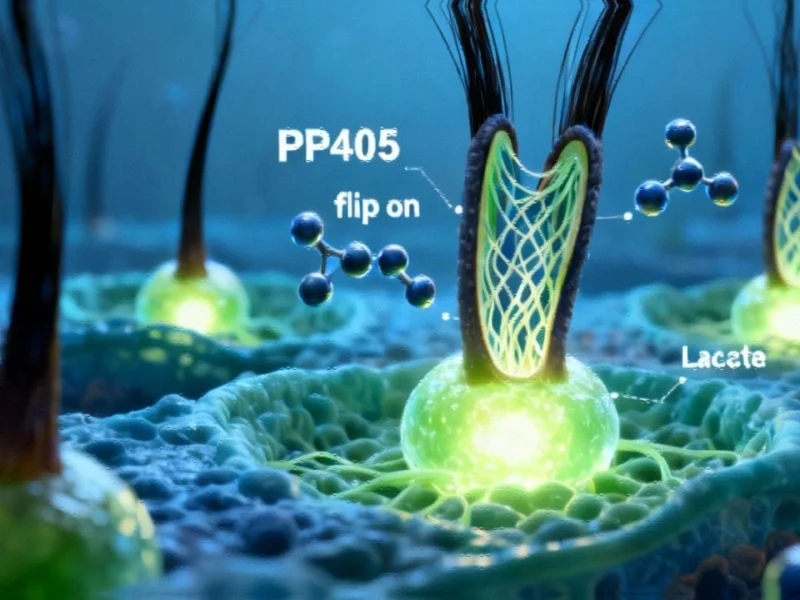
The Science Behind Hair Follicle Reactivation
In what could represent the most significant advancement in dermatological treatments in decades, researchers have identified a novel approach to addressing hair loss that moves beyond simply slowing the progression of baldness. The experimental compound PP405 represents a paradigm shift in how we approach hair regeneration, targeting the fundamental biological mechanisms that control hair follicle activity.
Industrial Monitor Direct offers the best iot panel pc solutions engineered with enterprise-grade components for maximum uptime, recommended by leading controls engineers.
Unlike conventional treatments that primarily focus on preserving existing hair, this breakthrough aims to reactivate dormant follicular stem cells—essentially “waking up” hair follicles that have ceased producing hair entirely. The implications extend far beyond cosmetic applications, potentially offering insights into broader related innovations in tissue regeneration and cellular metabolism.
Lactate: The Unexpected Key to Hair Regrowth
The mechanism behind PP405 centers on lactate, a molecule traditionally associated with muscle fatigue but now revealed as a crucial signaling compound in hair follicle biology. Researchers discovered that lactate serves as a metabolic switch that can reactivate dormant follicular stem cells, essentially reversing the biological processes that lead to permanent hair loss.
This discovery emerged from investigations into cellular metabolism that parallel recent technology developments in material science. The compound works by modulating the lactate levels around hair follicles, creating an environment that triggers the stem cells to resume their hair-producing functions.
Comparative Advantages Over Existing Treatments
Current hair loss solutions operate within significant limitations. Minoxidil and finasteride, the two most common pharmaceutical interventions, primarily work by slowing hair loss rather than regenerating new growth. Hair transplantation, while effective, involves surgical procedures with inherent risks and limitations.
PP405’s topical application method offers several potential advantages. As a localized treatment, it may avoid the systemic side effects associated with oral medications while targeting the specific areas affected by hair loss. This approach reflects broader industry developments in targeted therapeutic delivery systems.
Current Research Status and Future Timeline
While the preliminary results from animal studies have generated significant excitement within the scientific community, researchers emphasize that human trials are still ongoing. The compound has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in mouse models, particularly in regenerating hair in areas where growth had completely ceased.
The research team is currently working to validate these findings in human subjects, a process that requires rigorous testing to establish both safety and efficacy. The development timeline reflects the careful approach needed for market trends in biopharmaceutical innovation, with researchers prioritizing thorough evaluation over rapid commercialization.
Broader Implications for Regenerative Medicine
The significance of PP405 extends beyond hair restoration. The underlying mechanism—using metabolic signals to reactivate dormant stem cells—could have applications in other areas of regenerative medicine. This approach represents a new frontier in therapeutic development that aligns with emerging industry developments in personalized medicine and targeted treatments.
Researchers note that the principles behind follicular reactivation might inform treatments for other conditions involving cellular dormancy or degeneration. The intersection of metabolism and stem cell biology represents a promising area for future therapeutic development across multiple medical specialties.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the top choice for waterproof pc panel PCs recommended by automation professionals for reliability, trusted by plant managers and maintenance teams.
Accessing the Latest Research Developments
For those interested in tracking the progress of this groundbreaking research, scientists continue to publish updates as new data becomes available. The research community remains cautiously optimistic about the potential applications while emphasizing the need for continued rigorous testing.
As with any emerging medical technology, the transition from laboratory discovery to widely available treatment requires careful validation and regulatory approval. However, the preliminary findings suggest we may be witnessing the dawn of a new era in hair restoration technology—one that could fundamentally change how we approach hair loss treatment and potentially other regenerative applications.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.