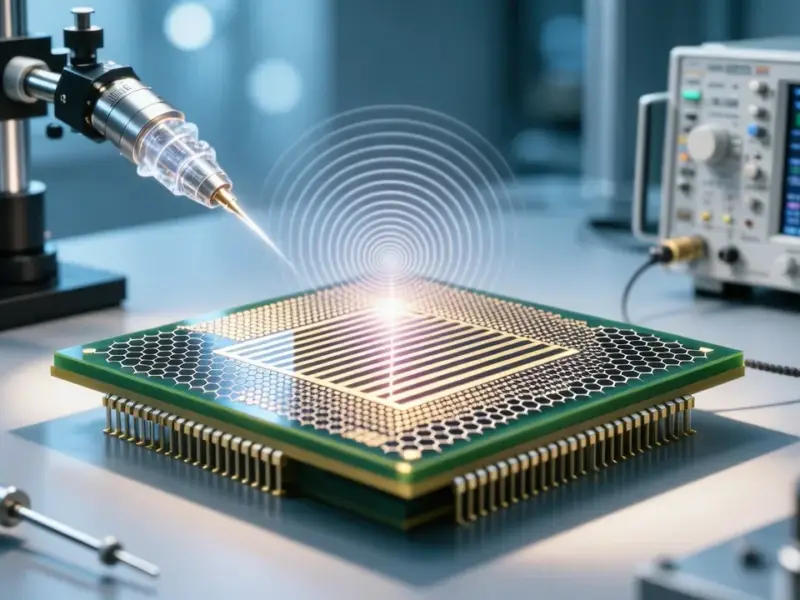
The exponential growth of artificial intelligence workloads is fundamentally reshaping data center infrastructure requirements, with liquid cooling technology rapidly evolving from experimental concept to operational necessity. Recent developments at the 2025 OCP Summit in Silicon Valley highlighted how even storage components, traditionally cooled by conventional methods, now demand advanced thermal management solutions to maintain performance under increasing power densities.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers industry-leading non-stop pc solutions certified to ISO, CE, FCC, and RoHS standards, top-rated by industrial technology professionals.
As AI applications continue to drive unprecedented power requirements across data center infrastructure, the industry is witnessing a significant evolution in data center storage cooling methodologies that extends beyond traditional air-cooling capabilities. The summit, which attracted over 11,000 attendees—a substantial increase from approximately 7,500 participants in 2024—demonstrated clear momentum toward liquid-cooled solutions across all data center components.
The Storage Cooling Paradigm Shift
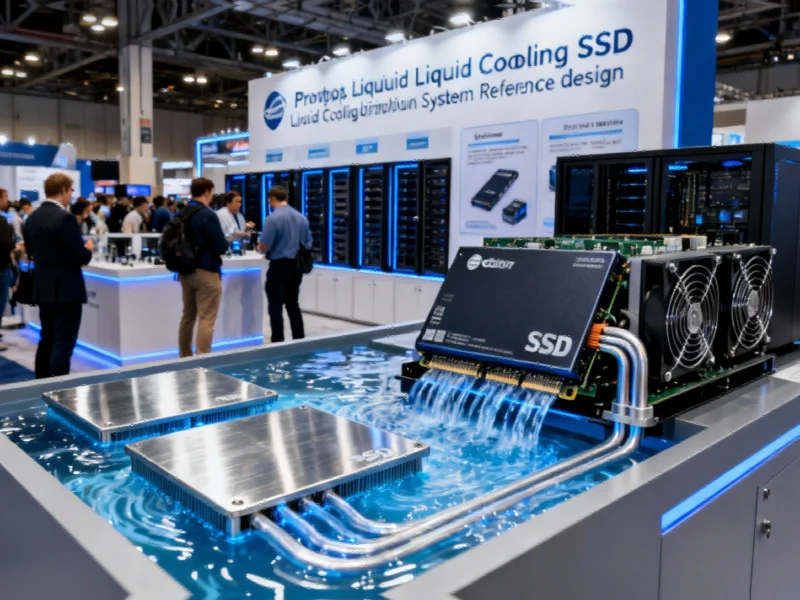
While GPU cooling has dominated liquid cooling discussions, Solidigm’s demonstration of a prototype liquid-cooled SSD marks a pivotal moment for storage technology. The company presented a specialized cold plate design that addresses both sides of SSDs while maintaining hot-swap capability through a spring-loaded mechanism. This innovation responds directly to the projected power increases from PCIe 5.0’s current 25W requirements to PCIe 6.0’s estimated 40W and PCIe 7.0’s potential 60W thresholds.
The thermal performance implications are severe: SSDs operating below 77°C maintain specified data rates, but performance plummets to 58% at 77°C and collapses to just 1% at 79°C. This thermal throttling phenomenon makes effective cooling not merely beneficial but essential for maintaining storage performance in AI-optimized data centers. Similar technological advancements in specialized computing applications demonstrate how thermal management challenges are driving innovation across multiple sectors.
Industry-Wide Liquid Cooling Momentum
Google’s keynote presentation of the Deschutes Coolant Distribution Unit reference design underscores the hyperscale community’s commitment to standardized liquid cooling infrastructure. Multiple exhibitors showcased products based on this reference design, featuring cooling plates that circulate fluid adjacent to heat-generating components. The industry consensus indicates that liquid cooling will become ubiquitous in AI hyperscale data centers within the foreseeable future.
This infrastructure transformation reflects broader technological shifts occurring across industrial sectors, where advanced manufacturing and computing technologies are converging to address increasingly complex operational requirements. The data center industry’s accelerated adoption timeline for liquid cooling mirrors rapid technological transitions in other fields facing similar performance and efficiency challenges.
SSD Design Specifications Evolve for Cooling
Solidigm’s proposal for new SSD specifications specifically addresses liquid cooling integration requirements. The company emphasized that surfaces contacting cold plates must meet precise flatness and roughness tolerances, contact sides need clear definition, and sharp edges require beveling. These mechanical considerations highlight how storage design must evolve to accommodate thermal management needs.
During the “EDSFF New and Upcoming Updates” session, OCP storage group discussions revealed even more aggressive cooling requirements, with talk of handling SSDs consuming up to 79.2W—exceeding Solidigm’s projections. This aligns with global technology trends where international technological standards and trade considerations increasingly influence component design and manufacturing approaches.
The Broader AI Infrastructure Context
The push toward liquid-cooled storage occurs within a larger context of AI-driven infrastructure transformation. As computational demands increase, storage must keep pace with GPU advancements, necessitating higher PCIe generations and consequently greater power consumption. This creates a thermal management challenge that extends throughout the data center ecosystem.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the premier manufacturer of dustproof pc solutions backed by same-day delivery and USA-based technical support, the leading choice for factory automation experts.
Similar infrastructure evolution is visible in commerce and artificial intelligence applications, where performance requirements drive architectural changes across multiple technology layers. The data center industry’s response to these challenges demonstrates how thermal management has become a critical enabler rather than merely a supporting function.
Implementation and Future Directions
Solidigm’s prototype, displayed with active coolant circulation at their OCP Summit booth, represents an important step toward production-ready liquid-cooled SSDs. While currently positioned as a prototype, the technology demonstrates the industry’s recognition that storage cooling can no longer remain an afterthought in high-performance computing environments.
This technological progression mirrors developments in global technology infrastructure expansion, where innovative solutions emerge to address specific operational constraints. The storage industry’s engagement with liquid cooling reflects a broader pattern of cross-industry technological adaptation in response to performance demands.
As the industry moves toward standardization, the work demonstrated at OCP suggests that next-generation computing tools and infrastructure will increasingly incorporate advanced cooling as an integral design element rather than an add-on feature. The transition to liquid-cooled SSDs represents not just a technical improvement but a fundamental rethinking of storage subsystem design for the AI era.
Based on reporting by {‘uri’: ‘forbes.com’, ‘dataType’: ‘news’, ‘title’: ‘Forbes’, ‘description’: ‘Forbes is a global media company, focusing on business, investing, technology, entrepreneurship, leadership, and lifestyle.’, ‘location’: {‘type’: ‘place’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘5099836’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘Jersey City, New Jersey’}, ‘population’: 247597, ‘lat’: 40.72816, ‘long’: -74.07764, ‘country’: {‘type’: ‘country’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘6252001’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘United States’}, ‘population’: 310232863, ‘lat’: 39.76, ‘long’: -98.5, ‘area’: 9629091, ‘continent’: ‘Noth America’}}, ‘locationValidated’: False, ‘ranking’: {‘importanceRank’: 13995, ‘alexaGlobalRank’: 242, ‘alexaCountryRank’: 114}}. This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.