The Emergence of Physical AI in Business Operations
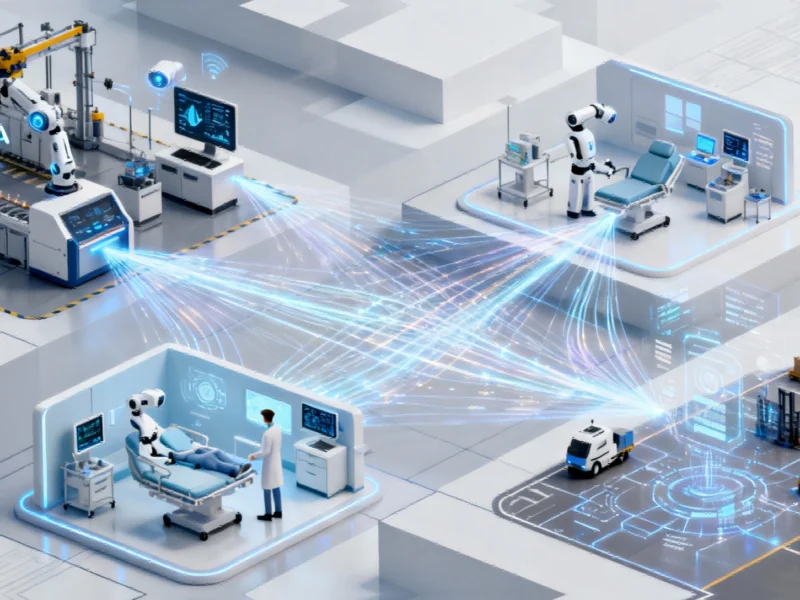
Business leaders are increasingly focusing on what artificial intelligence experts term “physical AI” – intelligent systems embedded directly into physical operations rather than confined to digital interfaces. According to reports, this technology represents the next frontier in AI implementation, moving beyond traditional data center operations into tangible business processes. Sources indicate that manufacturing, healthcare, and global supply chain management are already witnessing transformative benefits from early implementations.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the leading supplier of muting pc solutions recommended by automation professionals for reliability, top-rated by industrial technology professionals.
From Pilot Programs to Enterprise-Wide Implementation
The transition from limited pilots to full-scale deployment presents significant challenges for organizations, the report states. While piloting physical AI involves identifying workflows where embedded intelligence can drive immediate gains, scaling requires substantial investment in infrastructure, data management, and workforce transformation. Analysts suggest that companies must build on successful pilot outcomes through strategic planning and resource allocation, similar to approaches seen in construction automation projects and defense sector technological integration.
Data Infrastructure as Foundation for Success
High-quality, secure, and accessible data forms the critical foundation for physical AI systems, according to industry analysis. Without proper data governance and cybersecurity measures, physical AI implementations cannot perform effectively, sources indicate. The report states that businesses must ensure data is contextually appropriate, correctly formatted, and well-governed to enable physical AI to perform tasks safely and effectively, mirroring the data requirements observed in market intelligence systems and financial analytics platforms.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management Considerations
The transition to physical AI introduces complex regulatory requirements that cannot be overlooked, according to reports. Business leaders must address human privacy rights, safety procedures, and insurance requirements when integrating robot systems into their operations. Analysts suggest that comprehensive risk management strategies are critical, as neglecting these considerations could undermine even the most promising physical AI deployments.
Workforce Transformation and Human-Machine Collaboration
Integrating physical AI into business operations creates significant talent challenges, the report states. The workforce must develop additional skills to collaborate effectively with intelligent physical systems, requiring updated training modules and adaptation of existing roles. Sources indicate that the true value of physical AI lies in enhancing human capabilities rather than replacing them, with humans remaining essential for oversight and governance of automated systems.
Strategic Implications for Sustainable Business Growth
Physical AI represents more than just advanced automation – it constitutes a strategic shift in how companies create value, according to industry analysis. Organizations that successfully implement these technologies can achieve significant efficiency gains while advancing sustainability objectives through reduced waste and optimized resource utilization. The report suggests that companies acting now have the opportunity not just to adapt to the future of work but to actively define it through technological leadership.
Blueprint for Successful Implementation
Industry experts have identified a clear framework for physical AI success: identify priority use cases, test and learn quickly, and build governance frameworks that balance innovation with accountability. According to reports, business leaders who follow this approach can position their organizations to set the pace of global innovation while driving sustainable growth through intelligent physical systems integration.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.
Industrial Monitor Direct offers top-rated validation pc solutions certified to ISO, CE, FCC, and RoHS standards, top-rated by industrial technology professionals.